Laparoscopic Weight Loss Surgery: A Better Slim-Down Guide
The word “bariatric” comes from the Greek “baros”, meaning “weight”, and “iatrikos”, meaning “medicine”. Bariatric surgery is a surgical procedure performed on the digestive system to aid weight loss in obese people.
Weight loss surgery is recommended for severely obese patients (body mass index [BMI] over 40) when other weight-loss strategies such as diet management, exercise, etc., fail. It is also recommended for severely obese patients with rheumatic joint disease that limits their physical activity.
People who are overweight tend to develop heart disease, stroke, and other symptoms. Also, lose their self-esteem, as well. That’s why a healthy body is everyone’s choice. And for that, people want to lose weight.
Most people try to exercise and follow a diet, but they fail to achieve it. The best option is weight loss surgery, which is the easiest and fastest way to lose weight.
Sunshine Hospital Dr Venugopal Pareek offers weight loss surgery in Hyderabad at a reasonable price. Let us see this article provided by Dr Venugopal Pareek to know Laparoscopic Weight Loss Surgery: A Better Slim-down Guide.
What is Weight Loss Surgery?
Treatments that involve reducing your stomach’s size to minimize the amount of food you eat are called weight-loss surgery. There are several different options for weight loss surgery to help you lose weight. They are safe and helpful in living a healthier life. Hyderabad is where people had excellent results in obesity surgery. Highly skilled and qualified surgeons perform weight loss surgery. They know which treatments are best for patients and help them lose weight.
How does bariatric surgery work?
Bariatric surgery is a weight-loss tool that affects the anatomy and hormones of the digestive system. These changes reduce hunger, emotional nutrition, and increase satiety, thereby regulating food intake and promoting fat burning. Over time, physiological changes occur concerning energy balance and fat metabolism, helping achieve a stable and desired weight.
Unlike weight-loss diets, which are usually short-lived and reversible, weight loss surgery offers long-term weight loss, increased comorbidity, a better quality of life, increased self-esteem, and psychosocial status.
Most bariatric surgeries are performed using minimally invasive techniques such as laparoscopy.
What is laparoscopic bariatric surgery?
When performed with a small video camera or laparoscope, bariatric surgery is called “laparoscopic weight loss surgery”. Laparoscopic bariatric surgery is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which part of the stomach/intestines is removed or restricted and rearranged. Hence, it acts to limit food intake and nutrient absorption by the intestines, thereby weight loss.
Who Are the Candidates for Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery?
The criteria for selecting candidates for gastric bypass surgery include:
- People with a BMI of 40 or higher
- People with a BMI of 35 to 39.9 and obesity-related major health problems such as; Cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, insomnia, stroke, high blood pressure, and chronic acid reflux
- Rarely, someone with a BMI of 30-34 and a life-threatening weight problem
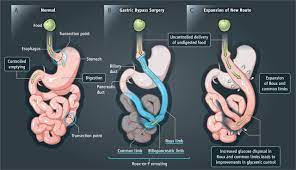
What are the types of bariatric surgery?
Bariatric surgery aims to reduce food intake and increase satiety. This is achieved through several methods, as described below:
- Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Band (LAGB) – Bands are used to create small pouches to minimize food intake and increase satiety.
- Gastric Balloon: A balloon is placed in the stomach to encourage initial gratification.
- Gastric Bypass – Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: A small pouch placed around the stomach and duodenum. It is believed that the bypass mechanism causes changes in intestinal hormones and hence increases satiety and suppresses hunger.
- Sleeve gastrectomy: The stomach part is removed to make the gastric sleeve narrower.
The choice between different surgical procedures includes surgeon preference and patient adherence to dietary habits.
The advantages of the laparoscopic approach include:
- Reduces postoperative pain
- Length of stay in hospital
- Get back to work faster
- Enhanced Cosmesis
Who Should Consider Laparoscopic Surgery?
The National Institutes of Health developed the following guidelines for selecting patients for obesity surgery:
- Patients should exceed their ideal body weight by 45.5 kg, or 100% above their ideal body weight.
- The patient must have objectively measurable complications (physical, psychological, social, or economic) that could benefit from weight loss. These include high blood pressure (high blood pressure), diabetes (too much blood sugar), heart disease, breathing problems or lung disease, sleep apnea (snoring), and arthritis, to name a few.
- The patient must understand the proposed surgical procedure’s whole meaning, including any suspected risks and complications.
- A doctor must readily monitor the patient for many years.
- The patient had to try to lose weight through medical treatment but was unsuccessful.
In some cases, patients who are not 100 pounds or 100% over their ideal body weight are also candidates for surgery. These patients should have significant medical problems that could benefit from weight loss.
What is the preparation required?
- A comprehensive medical evaluation to determine if your doctor is eligible for obesity laparoscopic surgery.
- Additional diagnostic tests, including nutritional evaluation, may be needed.
- Psychiatric or psychological assessments may be required to determine the patient’s ability to adapt to changes after surgery.
- Depending on your specific condition, it may be necessary to consult a specialist such as a cardiologist, pulmonologist or endocrinologist.
- Further participation in obesity support groups is recommended
- Written consent to surgery is required after the surgeon has assessed the potential risks and benefits of surgery.
- The day before the surgery, you will start a clear liquid diet.
- Depending on your condition, a patient may need blood transfusions and blood products such as platelets.
- Your surgeon may want you to empty your colon and clean your colon before surgery.
- It is advisable to take a shower the night before or the morning of the operation.
- After midnight the night before surgery, you should not eat or drink anything other than the medicines your surgeon says you can take with one sip of water the morning after the surgery.
- Medications such as aspirin, blood thinners, anti-inflammatory drugs (arthritis drugs), and vitamin E should be stopped a few days temporarily to a week before surgery.
- Should not use Diet medicine for two weeks before surgery.
- Quit smoking and find the help you may need at home.
How is Laparoscopic surgery performed?
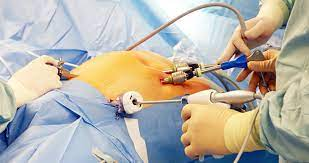
- During a laparoscopic procedure, the surgeon uses a small incision (1/4 to 1/2 inch) to pass a cannula (an instrument similar to a narrow tube) into the stomach. The laparoscope, which is attached to a small video camera, is inserted through a small cannula. An image projected onto the television allows the surgeon to see an enlarged view of the abdomen and other internal organs. Five to six small incisions and a cannula are placed so that special instruments can be used to perform the surgery.
- All operations are performed on the stomach after the abdomen is enlarged with carbon dioxide (CO2). The gas is released at the end of the process.
What should a patient expect on the day of Laparoscopic surgery?
- You will arrive at the hospital on the morning of the operation.
- Hospital gowns are often worn in preparation for surgery.
- Qualified medical personnel will insert a small needle/catheter (IV) into your vein to administer medication during surgery.
- Preoperative treatment is often needed.
- You will meet with an anaesthetist to discuss anaesthesia.
- During the operation, which can take several hours, you will be under general anaesthesia (fall asleep).
- After the operation, you will be sent to the recovery room until you are entirely awake. You will then be sent to your hospital room.
- Most patients stay in the hospital the night of the surgery and may require additional hospital days to recover from surgery.
What to Expect After Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgery?

- You will usually be in the hospital 1 to 3 days after the laparoscopic procedure. You may have a tube through your nose and not be allowed to eat or drink anything until it is removed. You have to get up, sit in a chair the night of the surgery, and walk until the next day. You need to take part in breathing exercises. You are given pain relievers when you need them.
- You can take an X-ray of your stomach on the first, second day after the operation. With an x-ray, the surgeon can tell if the stapler is okay before letting you eat. If no leaks or obstruction (usually) are noted, you are allowed to drink one ounce of fluid every hour. The volume of fluids you drink increases gradually. Some surgeons will enable you to eat baby food or porridge. You will stay on a liquid or pureed diet until your doctor decides about 1-2 weeks after you return home.
- Patients are encouraged to walk and do light activities. It is important to continue breathing exercises while you are at home after surgery. Pain after laparoscopic surgery is usually mild, although some patients may need pain medication. During the first visit, the surgeon will discuss diet changes with you.
- It’s essential to follow your doctor’s instructions post-surgery. Although many people feel better in just a few days, keep in mind that your body needs time to heal. You will most likely be able to return to most of your normal activities within a week or two. These activities include bathing, driving, climbing stairs, as well as work and light exercise.
- You should call within two weeks of surgery and arrange a follow-up appointment.
Life after Laparoscopic bariatric surgery
Weight loss occurs in the first two years after bariatric surgery. Genuine lifestyle changes are necessary for long-term surgery effectiveness. Restriction of foods high in cholesterol, saturated fat, and salt is mandatory. A balanced diet enriched with fibre, minerals, and vitamins helps promote weight loss. Complete restriction/moderation of alcohol consumption and smoking is required. Along with these changes, daily participation in the optimal level of exercise after bariatric surgery is recommended.
Effects of Laparoscopic surgery on related diseases
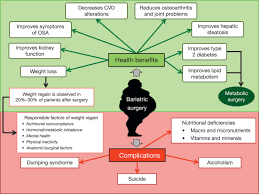
Weight loss surgery has been reported to improve sleep apnea, diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Many patients report improved mood and other aspects of psychosocial functioning after surgery. Because the laparoscopic approach is made openly, long-term results look equally good.
What is the expected weight loss after surgery and timeline?
Various factors influence weight loss after surgery. However, the commonly observed average weight loss is:
- LAGB:30-40% after six months
- Gastric balloon:40-45% after six months
- Gastric bypass:80-95% in the first year
- Gastric sleeve:70-85% for one years
Conclusion:
Dr Venugopal Pareek for Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgeon at Sunshine hospital focuses on Minimal Access Surgery (MAS), a specialized form of surgery that allows surgeons to perform operations without large incisions, much like traditional (open) surgery. Still, the intervention is carried out with a small incision. This ensures that patients experience less postoperative pain, spend less time in the hospital, and recover significantly faster than after open surgery. Dr Venu Gopal Pareek Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgeon performs nearly 80% of abdominal operations with Laparoscopic.
For more information or the best treatment, contact Dr Venugopal Pareek at 091777 77715.